Global phase III trials demonstrate that nerandomilast slowed lung function decline in IPF and PPF,

- Nerandomilast, an investigational agent, met the primary endpoint of both phase III trials, FIBRONEER™-IPF and FIBRONEER™-ILD, significantly reducing the decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) [mL] by absolute change from baseline at week 52, compared to placebo.1,2
- Nerandomilast’s safety and tolerability profile was consistent across both trials, with similar rates of permanent treatment discontinuation to placebo.1,2
- In both trials the composite key secondary endpoint (time to first acute IPF/ILD exacerbation, first hospitalization for respiratory cause, or death) was not met. However, in the FIBRONEER™-ILD trial, death occurred in a numerically smaller proportion of patients treated with nerandomilast than placebo.1,2
- New drug applications for nerandomilast in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) have been submitted in the US, China and the EU, with other geographies to follow.
Boehringer Ingelheim announced today detailed findings from the Phase III FIBRONEER™-IPF and FIBRONEER™-ILD trials. These studies evaluated nerandomilast, an investigational oral, preferential inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B), in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF), respectively, with and without background antifibrotic therapy. Results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine and also presented as a late-breaking abstract at the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2025 International Conference.
Nerandomilast is an investigational agent and has not been approved for use; its efficacy and safety has not been established.
Both trials met the primary endpoint at both doses, 9 mg and 18 mg, as measured by a reduction in the absolute change from baseline in forced vital capacity (FVC) [mL] decline at week 52 versus placebo.1,2 FVC is a measure of lung function.3
"After several challenges in the scientific community to bring forward new clinical data, IPF and PPF continue to take a devastating toll on patients,” said Toby Maher, M.D., Ph.D., Professor of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine, USC Los Angeles. “Having two phase III trials meet the primary endpoint is a major breakthrough for the scientific community, highlighting nerandomilast’s potential to have a meaningful impact on patients’ unmet needs, being studied as mono therapy or in combination with current treatments.”
Across both trials, similar rates of permanent treatment discontinuation to placebo were observed: In FIBRONEER™-IPF, adverse events led to permanent discontinuation of the trial regimen in 14.0% of the nerandomilast 18 mg group, 11.7% of the nerandomilast 9 mg group, and 10.7% of the placebo group.1,2 In FIBRONEER™-ILD, adverse events led to permanent discontinuation of the trial regimen in 10.0% of the nerandomilast 18 mg group, 8.1% in the nerandomilast 9 mg group, and 10.2% in the placebo group.2 In both trials there were no imbalances between the nerandomilast and placebo groups with respect to adverse events of special interest such as vasculitis, depression, suicidality, or drug induced liver injury.1,2
“Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and progressive pulmonary fibrosis are devastating conditions, with one in two people dying within five years of IPF diagnosis. Despite this stark reality, ongoing research may provide new possibilities for patients, as there remains a need for additional therapies,” said Shashank Deshpande, Head of Human Pharma and Member of the Board of Managing Directors at Boehringer Ingelheim. “The latest efficacy, safety and tolerability data on nerandomilast points to its potential in addressing the needs of those impacted by IPF and PPF.”
FIBRONEER™-IPF: Study Design and Results1
FIBRONEER™-IPF (NCT05321069) was a Phase III, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of nerandomilast over at least 52 weeks in patients with IPF. A total of 1,177 patients across 36 countries were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to receive nerandomilast 9 mg twice-daily (n=392), nerandomilast 18 mg twice-daily (n=392), or placebo twice-daily (n=393). Randomization was stratified by use of background antifibrotic therapy, with 77.7% receiving nintedanib or pirfenidone at enrollment.
Key efficacy results at 52 weeks, as published in the New England Journal of Medicine, include:
| Placebo |
Nerandomilast 9 mg twice-daily |
Nerandomilast 18 mg twice-daily |
|
| Primary Endpoint (adjusted mean change from baseline in FVC) | |||
| All patients |
−183.5 mL (n=391) (95% confidence interval [CI]: |
−138.6 mL (n=390) (95% CI: -165.6 to -111.6) |
−114.7 mL (n=392) (95% CI: -141.8 to - 87.5) |
|
Subgroups of Primary Endpoint (adjusted mean change from baseline in FVC)* *Trial was not powered to show a difference for these subgroups |
|||
| No background antifibrotic therapy | −148.7 mL (n=87) | −70.4 mL (n=86) | −79.2 mL (n=87) |
| Background nintedanib |
−191.6 mL (n=172) | −130.7 mL (n=184) | −118.5 mL (n=178) |
| Background pirfenidone | −197.0 mL (n=132) | −201.8 mL (n=120) | −133.7 mL (n=127) |
The composite key secondary endpoint (time to first acute IPF exacerbation, first hospitalization for respiratory cause, or death) was not met.
The most frequent adverse event was diarrhea, reported in 16.0% of the placebo group, 31.1% of the nerandomilast 9 mg group, and 41.3% of the nerandomilast 18 mg group. The adverse event that most frequently led to discontinuation of the trial regimen was diarrhea, with 1.8% in the nerandomilast 9 mg group, 6.1%, in the nerandomilast 18 mg group, and in 0.5% in the placebo group discontinuing treatment. Other adverse events were balanced across treatment groups, specifically showing no imbalances between the nerandomilast and placebo groups in adverse events of special interest such as vasculitis, depression, suicidality, or drug-induced liver injury. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation more frequently among patients taking background antifibrotic therapy across treatment groups. Serious adverse events occurred in 33%, 31%, and 30% of patients treated with placebo, nerandomilast 9 mg, and nerandomilast 18 mg, respectively. Adverse events were fatal in 5%, 4%, and 2% of patients treated with placebo, nerandomilast 9 mg, and nerandomilast 18 mg, respectively.
FIBRONEER™-ILD: Study Design and Results2
FIBRONEER™-ILD (NCT05321082) was a Phase III, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of nerandomilast over at least 52 weeks in patients with PPF. A total of 1,176 patients across 44 countries were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to receive nerandomilast 9 mg twice-daily (n=393), nerandomilast 18 mg twice-daily (n=391), or placebo twice-daily (n=392). Randomization was stratified by use of background antifibrotic therapy, with 43.5% receiving nintedanib.
Key efficacy results at 52 weeks, as published in the New England Journal of Medicine, include:
| Placebo |
Nerandomilast 9 mg twice-daily |
Nerandomilast 18 mg twice-daily |
|
| Primary Endpoint (adjusted mean change from baseline in FVC) | |||
| All patients |
−165.8 mL (n=391) (95% CI: -190.5 to -141.0) |
−84.6 mL (n=390) (95% CI: -109.6 to -59.7) |
−98.6 mL (n=390) (95% CI: -123.7 to -73.4) |
|
Subgroups of Primary Endpoint (adjusted mean change from baseline in FVC)* *Trial was not powered to show a difference for these subgroups |
|||
| No background |
−154.1 mL (n=222) (95% CI: -187.1 to -121.2) |
−82.3 mL (n=217) (95% CI: -115.9 to -48.8) |
−95.2 mL (n=220) (95% CI: -128.6 to -61.9) |
| Background nintedanib† |
−180.9 mL (n=169) (95% CI: -218.6 to -143.2) |
−87.8 mL (n=173) (95% CI: -125.4 to -50.2) |
−102.9 mL (n=170) (95% CI: -141.2 to -64.5) |
†2 patients in this group took pirfenidone rather than nintedanib. These were classified as protocol deviations, but the data from these patients were analyzed as part of the background nintedanib group.
Nerandomilast was not statistically significant for the composite key secondary endpoint (time to first acute exacerbation, hospitalization for a respiratory cause, or death), but there were numerically fewer deaths in both treatment groups: 9 mg group (n=33/8.4%), 18 mg group (n=24/6.1%), versus placebo (n=50/12.8%).
The safety and tolerability profile of nerandomilast was largely consistent with FIBRONEER™-IPF. The most frequent adverse event was diarrhea, reported in 24.7% of the placebo group, 29.5% of the nerandomilast 9 mg twice daily group, and 36.6% of the nerandomilast 18 mg twice daily group over 52 weeks. There were no imbalances between the nerandomilast and placebo groups in adverse events of special interest such as vasculitis, depression, or suicidality. The adverse events that most frequently led to treatment discontinuation were ‘condition aggravated’ (i.e., worsening of pulmonary fibrosis) which led to discontinuation in 1.5% in the nerandomilast 9 mg group, 1.0%, in the nerandomilast 18 mg group, and in 3.1% in the placebo group, and diarrhea, which led to discontinuation in 1.3%, 2.6%, and 0.5% of these treatment groups, respectively. The incidence of adverse events that led to treatment discontinuation was generally similar among patients taking background nintedanib therapy and patients not taking background nintedanib therapy. Serious adverse events occurred in 35.2%, 31.8%, and 33.2% of patients treated with placebo, nerandomilast 9 mg, and nerandomilast 18 mg, respectively. Adverse events were fatal in 5.1%, 3.6%, and 2.0% of patients treated with placebo, nerandomilast 9 mg, and nerandomilast 18 mg, respectively.
About nerandomilast
Nerandomilast (BI 1015550) is an investigational orally administered preferential inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) that is being studied as a potential treatment for IPF and PPF.1,2
Nerandomilast was granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of IPF in February 2022 and for the treatment of PPF in April 2025. The U.S. FDA recently granted priority review to the New Drug Application (NDA) for nerandomilast in IPF, with an anticipated action date in the fourth quarter of 2025. An NDA for nerandomilast in PPF has also been filed with the FDA. Regulatory submissions for nerandomilast in IPF and PPF are also under review in China and the EU, with filings in other geographies to follow.
About IPF and PPF
IPF is one of the more common progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (ILDs).4 In IPF, the root cause of pulmonary fibrosis is not known. Symptoms of IPF include breathlessness during activity, a dry and persistent cough, fatigue and weakness.5 The disease primarily affects patients over the age of 50 and affects more men than women.5
Patients with certain types of non-IPF fibrosing ILD may also develop a progressive phenotype known as PPF. In PPF, there is often a known underlying disease (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis or systemic sclerosis) cause for the ILD.6 In ILDs other than IPF, PPF is defined by worsening respiratory symptoms, physiological evidence of disease progression and radiological evidence of disease progression.6
The prevalence of IPF and PPF varies by region. It is estimated that up to 3.6 million people could be affected by IPF worldwide and up to 5.6 million by PPF.7,8
About Boehringer Ingelheim
Boehringer Ingelheim is a biopharmaceutical company active in both human and animal health. As one of the industry’s top investors in Research and Development, the company focuses on developing innovative therapies in areas of high unmet medical need. Independent since its foundation in 1885, Boehringer takes a long-term perspective, embedding sustainability along the entire value chain. More than 54,500 employees serve over 130 markets to build a healthier, more sustainable, and equitable tomorrow. Learn more at http://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/uk (UK) or www.boehringer-ingelheim.com (rest of world).
References
1Richeldi L, et al. (2025) Nerandomilast in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. In: NEJM. 2025.
2Maher TM, et al. (2025) Nerandomilast in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis. In: NEJM. 2025.
3Twisk JWR et al. (1998). Tracking of lung function parameters and the longitudinal relationship with lifestyle. European Respiratory Journal. 12(3):627–634.
4Sauleda J, et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epidemiology, Natural History, Phenotypes. Med Sci (Basel). 2018 Nov 29;6(4):110. doi: 10.3390/medsci6040110. PMID: 30501130; PMCID: PMC6313500.
5European Lung Foundation (2023) IPF - Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Accessed April 2025. Available at: https://europeanlung.org/en/information-hub/factsheets/ipf-idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis/.
6Podolanczuk AJ, Fernández Peréz ER. Identification, course, and management of progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Manag Care. 2024 Oct;30(7 Suppl):S122-S130. doi: 10.37765/ajmc.2024.89634. PMID: 39495032.
7Maher TM, Bendstrup E, Dron L, Langley J, Smith G, Khalid JM, Patel H, Kreuter M. Global incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2021 Jul 7;22(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01791-z. PMID: 34233665; PMCID: PMC8261998.
8Cottin V, Teague R, Nicholson L, Langham S, Baldwin M. The Burden of Progressive-Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 1;9:799912. Doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.799912. PMID: 35178411; PMCID: PMC8843847. Assuming a world population of 8bn
- “行走”的陈坤:我永远想成为一个比现在更好的演员
- Ascom launches Activity Monitoring, an innovative software solution for long-term care homes
- 中国科技第一展 高交会-第26届中国国际高新技术成果交易会
- 临商银行罗庄支行积极倡导勤俭节约,反对铺张浪费
- 新濠于《香港澳门米其林指南2025》再度勇夺全澳最多米其林星
- “奋进新时代 美丽追梦人”——谭木匠木梳走进北京故宫博物院
- 2024亚非贸易投资合作圆桌会议在北京举行
- 芬兰儿童权利非政府组织Protect Children的最新研究揭示了犯罪分子如何利用技术平台对儿童进行在线性虐待
- 知行传播:全渠道媒介资源 以专业高效服务助力品牌传播
- WS科技商业的魔法时刻:WhatsApp工具,科技魔法师揭示市场趋势的奇异秘密
- 从华南医信大会看趋势|霄云科技「影像数据存储解决方案」为何受三甲医院青睐
- Sidus Heroes:构建太空主题的元宇宙世界,重塑 Web3 游戏的未来
- 规模创历史新高,第二十六届全国影片推介会超160部!红色电影《浴血困牛山》惊艳亮相!
- 春节快乐阖家安康 携手贡乃享受节日美味
- Itron将Aquadis+容积式水表生产扩展到印度尼西亚
- 熊大爷全国生产基地开始筹建,扩张战略加速启航
- Mahindra & Mahindra选择Kinaxis来为不断增长的汽车产品组合提高供应链效率
- Newmont发布2023年可持续发展报告和2023年税收与特许权使用费报告
- CMG第二届中国电视剧年度盛典 留白影视《狂飙》斩获6项荣誉
- 首入华南 与君共鉴 I 君禾佛山五金机电仓储中心盛势开业!
推荐
-
 看新东方创始人俞敏洪如何回应董宇辉新号分流的?
(来源:中国证券报)
东方甄选净利润大幅下滑
资讯
看新东方创始人俞敏洪如何回应董宇辉新号分流的?
(来源:中国证券报)
东方甄选净利润大幅下滑
资讯
-
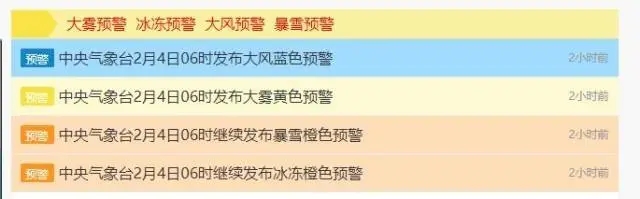 中央气象台连发四则气象灾害预警
暴雪橙色预警+冰冻橙色预警+大雾黄色预警+
资讯
中央气象台连发四则气象灾害预警
暴雪橙色预警+冰冻橙色预警+大雾黄色预警+
资讯
-
 奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒出近照 时隔473天更新动态!
2月20日凌晨2点,奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒
资讯
奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒出近照 时隔473天更新动态!
2月20日凌晨2点,奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒
资讯
-
 周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸引了不少素人和足球爱好者前来参加
周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸
资讯
周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸引了不少素人和足球爱好者前来参加
周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸
资讯
-
 一个“江浙沪人家的孩子已经不卷学习了”的新闻引发议论纷纷
星标★
来源:桌子的生活观(ID:zzdshg)
没
资讯
一个“江浙沪人家的孩子已经不卷学习了”的新闻引发议论纷纷
星标★
来源:桌子的生活观(ID:zzdshg)
没
资讯
-
 大家一起关注新疆乌什7.1级地震救援见闻
看到热气腾腾的抓饭马上就要出锅、村里大家
资讯
大家一起关注新疆乌什7.1级地震救援见闻
看到热气腾腾的抓饭马上就要出锅、村里大家
资讯
-
 王自如被强制执行3383万
据中国执行信息公开网消息,近期,王自如新增一
资讯
王自如被强制执行3383万
据中国执行信息公开网消息,近期,王自如新增一
资讯
-
 私域反哺公域一周带火一家店!
三四线城市奶茶品牌茶尖尖两年时间做到GMV
资讯
私域反哺公域一周带火一家店!
三四线城市奶茶品牌茶尖尖两年时间做到GMV
资讯
-
 中国减排方案比西方更有优势
如今,人为造成的全球变暖是每个人都关注的问
资讯
中国减排方案比西方更有优势
如今,人为造成的全球变暖是每个人都关注的问
资讯
-
 透过数据看城乡居民医保“含金量” 缴费标准是否合理?
记者从国家医保局了解到,近期,全国大部分地区
资讯
透过数据看城乡居民医保“含金量” 缴费标准是否合理?
记者从国家医保局了解到,近期,全国大部分地区
资讯

