Pooled data presented at ERS: nerandomilast monotherapy linked to nominally significant reduction in
- A new pooled analysis of the FIBRONEER™-IPF and FIBRONEER™-ILD trials resulted in a nominally significant reduction in the risk of death by 59% in patients who received 18mg nerandomilast without background therapy versus placebo.1
- Both FIBRONEER™ phase III trials, had met their primary endpoint (reduction of lung function decline measured in forced vital capacity) but did not meet their key secondary endpoint (risk of acute exacerbation, hospitalization for respiratory cause, or death).1-3
- Nerandomilast had a favorable safety and tolerability profile, with a similar rate of discontinuation due to adverse events as placebo.1-3
- Findings presented at ERS support previous clinical trial data on the safety and efficacy of nerandomilast in IPF and PPF as monotherapy and in combination with currently approved medications.1
Boehringer Ingelheim today announced new data from the global Phase III FIBRONEER™ program on nerandomilast, an investigational oral preferential PDE4B inhibitor, which is currently not approved for use. The new pooled analyses, the first to demonstrate a nominally significant reduction in risk of death across IPF and PPF, was presented in a poster at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) International Congress 2025 in Amsterdam. Nominal significance means that the trial results showed a clear trend that suggests a possible benefit; however, the evidence does not meet the strict criteria to declare it statistically significant.
Both phase III trials, FIBRONEER™-IPF and FIBRONEER™-ILD, had met their primary endpoint, demonstrating that nerandomilast slowed lung function decline in IPF and PPF, with similar discontinuation rates to placebo.2,3 Although both trials did not meet the key secondary endpoint (time to first acute IPF/ILD exacerbation, first hospitalization for respiratory cause, or death over duration of trial),2,3 the pooled analysis resulted in a nominally significant reduction in risk of death across IPF and PPF for the 18mg nerandomilast dose vs placebo in monotherapy and with background nintedanib.1 The trend was more pronounced in monotherapy.1
“The new pooled data zoom in on nerandomilast’s potential as monotherapy, pairing efficacy with a nominally significant reduction in the risk of death. While the findings are exploratory, they add to the growing body of evidence and may impact future research directions in pulmonary fibrosis,” said Marlies Wijsenbeek, Erasmus MC University Medical Centre. “The new findings go hand-in-hand with nerandomilast’s favorable safety and tolerability profile in previous studies. In a disease area with many patients discontinuing treatment,4 mostly related to limited tolerability of current therapies, this could really improve outcomes for patients.”
Findings of the pooled analysis
In both FIBRONEER™ trials, patients (FIBRONEER™-IPF, n=1177; FIBRONEER™-ILD, n=1176) were randomized to receive nerandomilast 9mg twice per day, 18mg twice per day, or placebo.2,3 The data was pooled and changes in FVC over 76 weeks and clinically relevant outcomes (acute exacerbations, respiratory hospitalization, and death) were analyzed. The analyses included the overall population and subgroups of patients by use of background therapy at baseline.1
In the overall trial population, a nominally significant reduction in the risk of death by 43% was observed in patients who received 18mg (HR 0.57 [CI: 0.41-0.78)].1 A nominally significant reduction in the risk of death, by 59%, was observed in patients who received 18mg nerandomilast without background therapy (HR 0.41 [CI: 0.24-0.70)].1 This downward trend was also seen in patients taking background nintedanib with a nominally significant reduction in the risk of death by 41% (HR 0.59 [CI: 0.37-0.94)].1
“For people living with pulmonary fibrosis, mortality remains unacceptably high, with every second person dying within 5 years of diagnosis,” said Shashank Deshpande, Chairman of the Board of Managing Directors and Head of Human Pharma at Boehringer Ingelheim. “As the first Phase III trial program to demonstrate a nominally significant reduction in the risk of death in progressive pulmonary fibrosis, FIBRONEER heralds a significant advance for this group of patients, who face a devastating diagnosis and very limited treatment options.”
In the pooled analysis, nerandomilast showed a favorable safety and tolerability profile, with a similar rate of discontinuation due to adverse events as placebo, consistent with the prior phase III results.1 The most frequent adverse event in the nerandomilast group without background therapy was diarrhea, reported in 14.6% in the placebo group, 17.5% in the nerandomilast 9 mg group, and 27.4% in the nerandomilast 18 mg group.1 Patients receiving either background nintedanib or pirfenidone reported diarrhea in 27.1% in the placebo group, in 41.9% in the 9mg nerandomilast group and in 47.7% in the 18mg nerandomilast group. In all patients, serious adverse events occurred in 44.7%, 39%, and 40.5% of patients treated with placebo, nerandomilast 9 mg, and nerandomilast 18 mg, respectively.1
These latest FIBRONEER™ findings reinforce nerandomilast’s potential as a new treatment for IPF and PPF.1
About nerandomilast
Nerandomilast (BI 1015550) is an investigational orally administered preferential inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) that is being studied as a potential treatment for IPF and PPF.2,3 Its efficacy and safety has not been established.
Nerandomilast was granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of IPF in February 2022 and for the treatment of PPF in April 2025.7,8 The FDA recently granted priority review to the New Drug Application (NDA) for nerandomilast in IPF, with an anticipated action date in Q4 2025. An NDA for nerandomilast in PPF has also been filed. Regulatory submissions are under review in China, the UK, and the EU, with filings in other geographies to follow.8
About IPF and PPF
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is one of the more common progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (ILDs), primarily affecting people over 50 and more men than women.9 It is associated with breathlessness, persistent cough, fatigue, and reduced survival. With approximately half of patients dying within five years of diagnosis,5,6 IPF is deadlier than many forms of cancer.10,11
Patients with other types of fibrosing ILD can also develop a progressive phenotype, termed progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF). PPF is defined by worsening respiratory symptoms, physiological and radiological progression, despite management of the underlying cause.12
Globally, up to 3.6 million people may be affected by IPF and up to 5.6 million by PPF.12,13
About Boehringer Ingelheim
Boehringer Ingelheim is a biopharmaceutical company active in both human and animal health. As one of the industry’s top investors in research and development, the company focuses on developing innovative therapies that can improve and extend lives in areas of high unmet medical need. Independent since its foundation in 1885, Boehringer takes a long-term perspective, embedding sustainability along the entire value chain. Our approximately 54,500 employees serve over 130 markets to build a healthier and more sustainable tomorrow. Learn more at http://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/uk (UK) or www.boehringer-ingelheim.com (rest of world).
References
- Oldham J, et al. (2025) Efficacy, safety and tolerability of nerandomilast in patients with pulmonary fibrosis: pooled data from the FIBRONEER-IPF and FIBRONEER-ILD trials. Poster, ERS 2025.
- Maher T et al. (2025) Nerandomilast in Patients with Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2025 Jun 12;392(22):2203-2214. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2503643.
- Richeldi L, et al. Nerandomilast in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2025 Jun 12;392(22):2193-2202. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2414108.
- Levra S et al. Long-term safety of antifibrotic drugs in IPF: a real-world experience. Biomedicines. 2022;10(12):3229. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123229.
- Zheng Q et al. The global burden and temporal trends of interstitial lung disease: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. ERJ Open Res. 2022;8(1):00591-2021. DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00591‑2021.
- Cen Z et al. Outcomes and predictors of progression in progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2382949. DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2406439.
- Boehringer Ingelheim (2022) FDA Grants BI 1015550 Breakthrough Therapy Designation for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Accessed September 2025. Available at: https://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/us/human-health/lung-diseases/pulmonary-fibrosis/fda-grants-bi-1015550-breakthrough-therapy.
- Boehringer Ingelheim (2025) Global phase III trials demonstrate that nerandomilast slowed lung function decline in IPF and PPF, with similar discontinuation rates to placebo. Accessed September 2025. Available at: https://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/human-health/lung-diseases/pulmonary-fibrosis/phase-3-trials-nerandomilast-slowed-lung-function-decline-ipf-and-ppf.
- European Lung Foundation (2023) IPF - Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Accessed April 2025. Available at: https://europeanlung.org/en/information-hub/factsheets/ipf-idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis/.
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2024;74(1):12–49. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21820.
- Vancheri C, Failla M, Crimi N, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a disease with similarities and links to cancer biology. Eur Respir J. 2010;35(3):496–504. DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00077309.
- Cottin V, Teague R, Nicholson L, Langham S, Baldwin M. The Burden of Progressive-Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 1;9:799912. Doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.799912. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.799912.
- Podolanczuk AJ et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: state of the art for 2023. Eur Respir J. 2023;61(4):2200957. DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00957‑2022.
- 农发行耒阳市支行:聚力打造“三大品牌”推动柜面服务提档升级
- 硅胶管的耐温性如何?能够承受多高的温度?
- 会议平板的新场景拓展,皓丽会议电视诞生的意义和价值
- 功不唐捐·行而不辍——书法名家刘冀龙百家媒体聚焦报道
- 于晓津:肠胃“堵车”有良方
- 联想控股料2024全年亏损收窄或扭亏为盈
- 互联网助力平顶山衣食住行焕发新活力!
- 律师们有福了,DS满血版加持下的AlphaGPT将带来超凡的办案体验
- 国内延时喷剂十大名牌之一,诺曼帝延时喷剂Normane官网
- “价值引领 绿动湖州”远程醇氢电动重卡打造绿色城建新生态
- Esri出版关于快速发展的移动GIS领域的新书
- SES Receives All Required Regulatory Approvals to Complete Intelsat Acquisition
- 甲流肆虐,奥司他韦携手步长宣肺败毒颗粒,共筑健康防线
- Alphawave Semi携手Teledyne LeCroy推出PCIeⓇ7.0 信号发生和测量技术
- 延安丹荟正式启动“牡丹产业消费帮扶”计划
- “一件事”里的改革故事|牡丹区免费帮办代办服务,助力餐饮店老板顺利开业
- 智能炒菜机也能复刻大师锅气?优特智厨G3-2.1四大系统全新升级
- 三河到蚌埠运输公司门到门服务整车零担
- 时光不老·温暖同行 拱墅区点亮“六个老有”,让银发生活更美好
- Q3 2024 Operations and Financial Update
- 平安守护者行动丨平安橙守护,共圆高考梦——平安产险黑龙江分公司2025年高考护航行动
- 海信中央空调强大工厂实力 成就品质“满分”
- 科技赋能保险新生态 旭飞云为您保驾护「行」
- 海能达亮相深圳大鹏应急“一园双基地”揭牌,培育和发展应急领域新质生产力
- 《掌心》定档2月7日开播,刘诗诗窦骁搭档破局复仇
- CE Channel,精准对接全球市场,助您实现国际业务扩张!
- 家政保洁服务:打造舒适宜居环境的首选
- GSL ENERGY:抢占全球工商业储能风口的3个黄金法则
- Lenovo在MWC上最新推出的ThinkPad和ThinkBook笔记本电脑为人工智能PC创新铺平道路
- Bitget 首席执行官 Gracy Chen 入选 CoinDesk “Web3 和 AI 领域 50 位杰出女性”榜单
推荐
-
 大家一起关注新疆乌什7.1级地震救援见闻
看到热气腾腾的抓饭马上就要出锅、村里大家
资讯
大家一起关注新疆乌什7.1级地震救援见闻
看到热气腾腾的抓饭马上就要出锅、村里大家
资讯
-
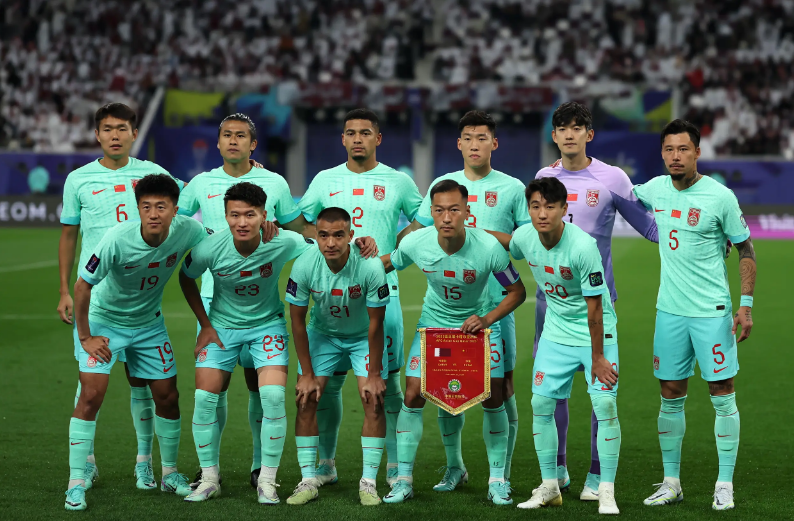 国足13次出战亚洲杯首次小组赛0进球
北京时间1月23日消息,2023亚洲杯小组
资讯
国足13次出战亚洲杯首次小组赛0进球
北京时间1月23日消息,2023亚洲杯小组
资讯
-
 看新东方创始人俞敏洪如何回应董宇辉新号分流的?
(来源:中国证券报)
东方甄选净利润大幅下滑
资讯
看新东方创始人俞敏洪如何回应董宇辉新号分流的?
(来源:中国证券报)
东方甄选净利润大幅下滑
资讯
-
 周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸引了不少素人和足球爱好者前来参加
周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸
资讯
周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸引了不少素人和足球爱好者前来参加
周星驰新片《少林女足》在台湾省举办海选,吸
资讯
-
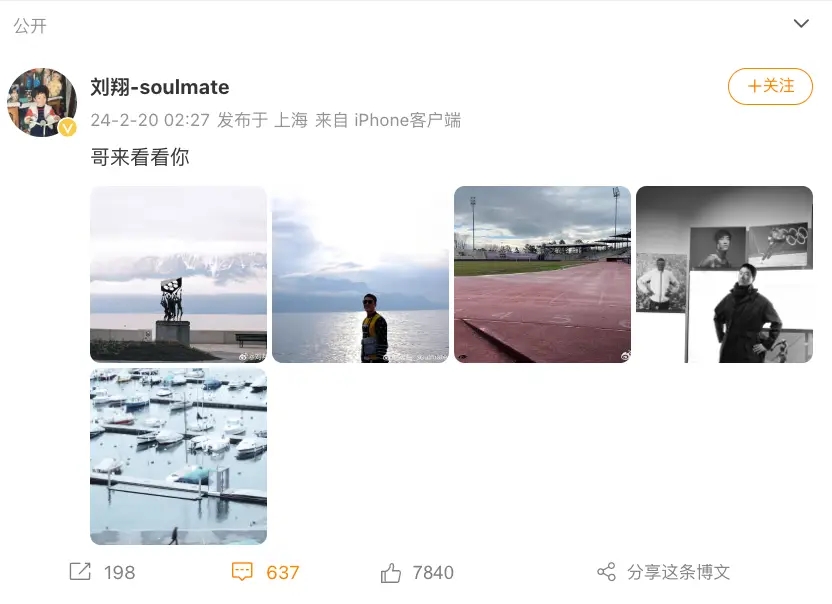 奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒出近照 时隔473天更新动态!
2月20日凌晨2点,奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒
资讯
奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒出近照 时隔473天更新动态!
2月20日凌晨2点,奥运冠军刘翔更新社交账号晒
资讯
-
 透过数据看城乡居民医保“含金量” 缴费标准是否合理?
记者从国家医保局了解到,近期,全国大部分地区
资讯
透过数据看城乡居民医保“含金量” 缴费标准是否合理?
记者从国家医保局了解到,近期,全国大部分地区
资讯
-
 王自如被强制执行3383万
据中国执行信息公开网消息,近期,王自如新增一
资讯
王自如被强制执行3383万
据中国执行信息公开网消息,近期,王自如新增一
资讯
-
 海南大学生返校机票贵 有什么好的解决办法吗?
近日,有网友在“人民网领导留言板&rdqu
资讯
海南大学生返校机票贵 有什么好的解决办法吗?
近日,有网友在“人民网领导留言板&rdqu
资讯
-
 男子“机闹”后航班取消,同机旅客准备集体起诉
1月4日,一男子大闹飞机致航班取消的新闻登上
资讯
男子“机闹”后航班取消,同机旅客准备集体起诉
1月4日,一男子大闹飞机致航班取消的新闻登上
资讯
-
 新增供热能力3200万平方米 新疆最大热电联产项目开工
昨天(26日),新疆最大的热电联产项目—&md
资讯
新增供热能力3200万平方米 新疆最大热电联产项目开工
昨天(26日),新疆最大的热电联产项目—&md
资讯

